Power On Self-Test — The Power On Self-Test (POST) is an automatic test that is run by your Mac's hardware each time your Mac powers up, before Mac OS X is loaded. POST checks the basic functioning of RAM, Processor and boot ROM. I/O Check — I/O Check monitors your system for input and output (I/O) errors. Sep 10, 2020 When we need to check disk, we use the utility called chkdsk, which is a Windows utility that can check the integrity of your hard disk and can fix various file systems. You can apply check disk (chkdsk) in my computer and Command Prompt, or use the alternative third-party disk checking tools to automatically scan and repair hard drive errors.
- Check My Mac For Errors Working
- Check My Mac For Errors Omissions
- Check For Errors Free
- Mac Error Codes
Mac OS X Snow Leopard offers a First Aid pane. This feature of Disk Utility lets you check almost any disk for errors, as well as repair any errors that it finds. Here are the two exceptions when the buttons are disabled:
The start-up disk: Disk Utility can't repair the start-up disk, which makes sense if you think about it, because that drive is currently being used.
If you have multiple operating systems on multiple disks, you can boot from another Mac OS X installation on another drive to check your current start-up disk. Or you can boot your system from the original Mac OS X installation DVD and run Disk Utility from the Installation menu.
Write-protected disks: Although you can use the Disk Utility to verify CDs and DVDs, Disk Utility can't repair them.
You usually can't repair a disk that has openfiles that are currently being used. If you're running an application from a drive or you've opened a document that's stored on that drive, you probably can't repair that drive.
In order to verify or repair, you must be logged in as an admin-level user.
You can also select to verify and repair permissions (or privileges) on a disk. If you can't save or move a file that you should be able to access, try checking that drive for permissions problems. Although you can't fix disk errors on a boot drive, you can verify and repair permissions on any volume that contains a Mac OS X installation (whether it was used to boot your Mac or not).
To verify or repair a drive, follow these steps:
Access the Applications folder, and then open the Utilities folder.
Open the First Aid pane.
The First Aid pane displays a list of volumes on your Mac.Select the target volume/partition in the list at the left.
Click the Verify Disk button
Snow Leopard checks the contents of the drive and displays any errors.
Click the Repair Disk button.
Snow Leopard verifies the contents of the drive and fixes any problems.
It's a good idea to check your disks once every two or three days. If your Mac is caught by a power failure or Mac OS X locks up, check disks after you restart your Mac.
A number of very good commercial disk repair utilities are on the market. However, Disk Utility does a good job on its own, and it's free.
Undoubtedly, there are lots of reasons that can lead to failed Mac boot. And hard disk error is one of them. So it is urgent to check out the disk errors and repair them in time while you encounter this problem. Otherwise, not only you cannot boot Mac, but also you will lose many important files or folder on Mac.
Fortunately, two built-in utilities have been created in Mac for the problem.
Way 1: Repair Disk Errors with Disk Utility in Mac Recovery Mode
As we know, while your Mac cannot boot normally, several boot options can help to fix problems. And utilities available in Mac recovery boot, such as Disk Utility, reinstall macOS etc could fix the disk issues. Now let's see how Disk Utility checks and repairs disk errors.
Step 1: Get to Disk Utility on Mac startup.
Start Mac in recovery mode and you could see four options that it provides to resolve hardware or software issues. Choose the Disk Utility and click Continue to open it.
Step 2: Choose the disk you need to repair.
In the left pane, there lists the Mac startup disk and other connected drives. Just click the corrupted or damaged disk from the left pane, or any other drives you want to repair.
Note:
Before checking and repairing disk errors, you can see the selected disk whether it can be verified or repaired by clicking 'Info' from top menu.
Step 3: Run First Aid to check and repair disk errors.

1. Click the First Aid on the top menu and tap on Run button to launch First Aid on Mac.
2. Continue while you get a prompting message from First Aid.
3. First Aid will run and check out the possible errors on preferred disk.
4. Click Done button to finish disk repairing when First Aid process is complete.

At last, you will get three results generally after First Aid process. Click the Show details to view.

Result 1: Nothing is wrong or no errors needed to be repaired.
Then you will receive message like 'The volume (the name of disk) appears to be OK'.
Result 2: You will get 'overlapped extent allocation' errors.
It means two or more files occupy the same space on your disk. Check each of them to see if you can replace or recreate it. If not, check the file content and decide if you can delete it.
Result 3: Get 'The underlying task reported failure' errors.
It means the disk has not been fully repaired. You need to run Disk Utility again and try to repair the damaged disk. If it cannot be done, make a backup of your data and then reformat the disk, and reinstall macOS. Or if the errors cannot be repaired because of physical damage, you will need to replace the old damaged disk.
Check My Mac For Errors Working
Note: Besides disk repair, you could also use Disk Utility in OS X recovery mode to wipe, or restore or partition disk.
Way 2: Repair Mac Hard Disk in Single User Mode
Besides Disk Utility in Mac recovery boot, there is also a built-in disk diagnostic and repair program called fsck or file system consistency check, which could verify the current startup disk and repair it. But in order to make full use of it via command line, you should enter Mac single user mode.
Step 1: Boot Mac in single user mode.
Turn on your Mac computer. When you hear the startup tone, press and hold on Command + S on the keyboard. Until you see a text-code black screen, release the keys. Now you have successfully access Mac in single user mode and just wait for it starting fully about few seconds.
Step 2: Check and repair current startup disk.
Generally, the last line should end in root# if Mac has booted successfully in single user mode. Now right after the root# prompt, enter the following command and press Return key.
/sbin/fsck -fy
Check My Mac For Errors Omissions
Wait for it to check your Mac's hard drive, such as check extents overflow file, catalog file, multi-linked files, catalog hierarchy, extended attributes file, volume bitmap or information. Lastly, you will be prompted 'The volume (name of your hard drive) appears to be OK' or 'FILE SYSTEM WAS MODIFIED'. Then you will see the root# prompt again.
Step 3: Reboot Mac and exit single use mode.
Enter the command 'reboot' and press Return key again. Then your Mac will restart normally from hard drive.
Tips:
It is worth mentioning that forgotten Mac admin password can be reset in recovery mode and single user mode. More details, please go for passage about how to reset Mac admin password if forgot.
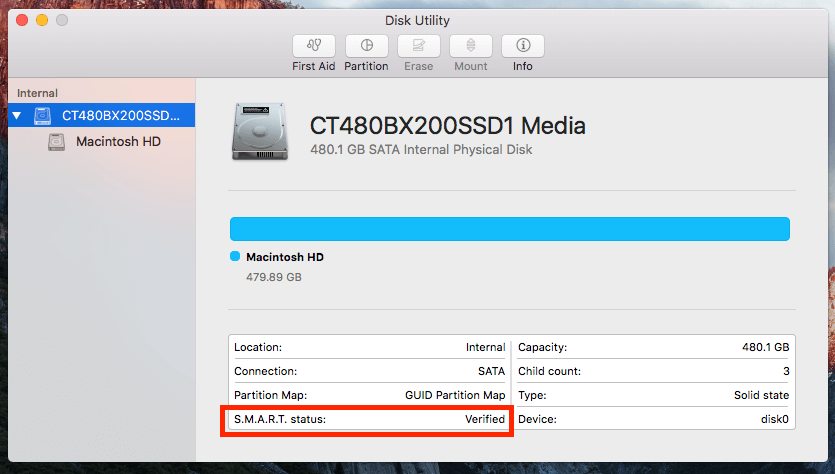
1. Click the First Aid on the top menu and tap on Run button to launch First Aid on Mac.
2. Continue while you get a prompting message from First Aid.
3. First Aid will run and check out the possible errors on preferred disk.
4. Click Done button to finish disk repairing when First Aid process is complete.
At last, you will get three results generally after First Aid process. Click the Show details to view.
Result 1: Nothing is wrong or no errors needed to be repaired.
Then you will receive message like 'The volume (the name of disk) appears to be OK'.
Result 2: You will get 'overlapped extent allocation' errors.
It means two or more files occupy the same space on your disk. Check each of them to see if you can replace or recreate it. If not, check the file content and decide if you can delete it.
Result 3: Get 'The underlying task reported failure' errors.
It means the disk has not been fully repaired. You need to run Disk Utility again and try to repair the damaged disk. If it cannot be done, make a backup of your data and then reformat the disk, and reinstall macOS. Or if the errors cannot be repaired because of physical damage, you will need to replace the old damaged disk.
Check My Mac For Errors Working
Note: Besides disk repair, you could also use Disk Utility in OS X recovery mode to wipe, or restore or partition disk.
Way 2: Repair Mac Hard Disk in Single User Mode
Besides Disk Utility in Mac recovery boot, there is also a built-in disk diagnostic and repair program called fsck or file system consistency check, which could verify the current startup disk and repair it. But in order to make full use of it via command line, you should enter Mac single user mode.
Step 1: Boot Mac in single user mode.
Turn on your Mac computer. When you hear the startup tone, press and hold on Command + S on the keyboard. Until you see a text-code black screen, release the keys. Now you have successfully access Mac in single user mode and just wait for it starting fully about few seconds.
Step 2: Check and repair current startup disk.
Generally, the last line should end in root# if Mac has booted successfully in single user mode. Now right after the root# prompt, enter the following command and press Return key.
/sbin/fsck -fy
Check My Mac For Errors Omissions
Wait for it to check your Mac's hard drive, such as check extents overflow file, catalog file, multi-linked files, catalog hierarchy, extended attributes file, volume bitmap or information. Lastly, you will be prompted 'The volume (name of your hard drive) appears to be OK' or 'FILE SYSTEM WAS MODIFIED'. Then you will see the root# prompt again.
Step 3: Reboot Mac and exit single use mode.
Enter the command 'reboot' and press Return key again. Then your Mac will restart normally from hard drive.
Tips:
It is worth mentioning that forgotten Mac admin password can be reset in recovery mode and single user mode. More details, please go for passage about how to reset Mac admin password if forgot.
Check For Errors Free
Mac Error Codes
Related Articles:
